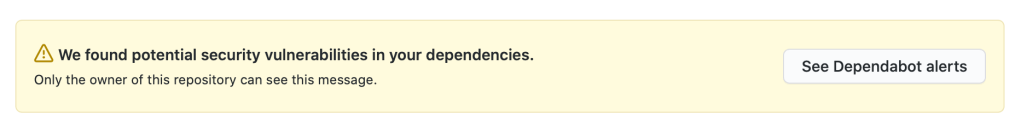
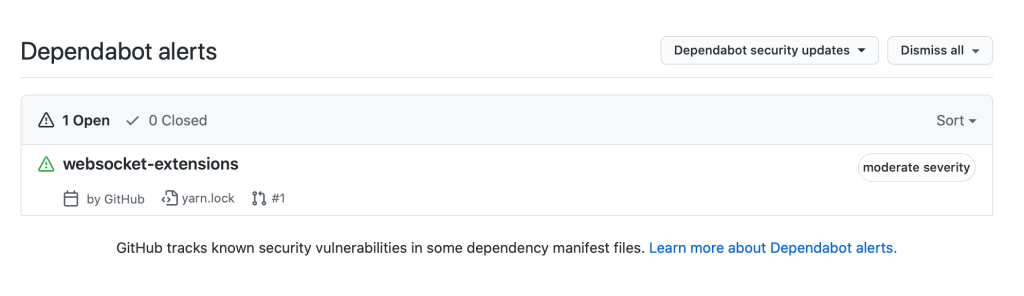
Whether you forgot to update a file or want to clean up your commit history, Git gives you powerful tools to change past commits. Here’s how to do it safely and effectively.
There are 2 sets of instructions:
- How to Change the Most Recent Commit
- How to Change an Older Commit (Not the Latest One)
Follow whichever set of instructions makes sense for your situation.
1. How to Change the Most Recent Commit
Step 1: Make your changes to the code
Make the changes you want to make to your code then run the git add command:
# Make your code changes
git add .Step 2: Add the changes to the latest commit
# Option 1: keeps the commit message the same
git commit --amend --no-edit
# Option 2: allows you to modify the commit messagegit commit --amend
git commit --amend without the --no-edit flag opens your editor so you can modify the commit message.
⚠️ Important: Only amend if the commit hasn’t been pushed to a shared branch. Amending a pushed commit rewrites history, which can mess with other collaborators.
2. How to Change an Older Commit (Not the Latest One)
Step 1: Start an interactive rebase
To edit an earlier commit (e.g., the second one back), use interactive rebase:
git rebase -i HEAD~nReplace n with how many commits back you want to go.
You’ll see something like:
pick a1b2c3 Fix login bug
pick d4e5f6 Update README
pick 789abc Add scraper moduleEach line represents a commit.
Step 2: Change pick to edit
Change pick to edit on the line you want to modify:
pick a1b2c3 Fix login bug
edit d4e5f6 Update README
pick 789abc Add scraper moduleThis tells Git: “Pause at this commit so I can change it.”
❓ What if nothing happens when you try to type?
If Git opens Vim (default for many systems), here’s how to use it:
- Press
ito enter Insert mode – now you can type. - Change
picktoeditas needed. - Press
Escto exit insert mode. - Save and exit by typing the following:
:wqThen press Enter.
Step 3: Git Pauses the Rebase
After saving, Git will stop at the commit you marked for editing. You’ll see a message like:
Stopped at d4e5f6... Update READMEStep 4: Make Your Changes
Make whatever changes you need to the code. Then:
git add .
git commit --amendYou can now update both the code and the message if you want.
Step 5: Continue the Rebase
Once you’re done:
git rebase --continueGit will resume the rebase and replay the rest of your commits.
Made a Mistake?
To cancel the rebase and go back:
git rebase --abort🧼 After Editing Commits: Push Carefully
If you’ve already pushed these commits to a remote branch, you’ll need to force push:
git push --force⚠️ Use with caution – force pushing can overwrite others’ work. Only do this on branches you own or after coordinating with teammates.